 |
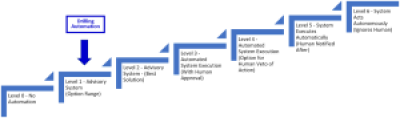
| Current level of Drilling Automation |
 |
| Abstract: SPE189636-MS |
Things I Think About
 |
| Current level of Drilling Automation |
 |
| Abstract: SPE189636-MS |
Today we are going to talk about a very specific subject: Starting a small business with a partner or partners.
The generally understood definition by the United States government for a small business is a business that employs less than 500 people. There are financial considerations that also go along with that, but I am not going to attempt to touch on those here.
With this in mind, the concept of the US economy being powered by small business makes a lot more sense. A large majority of businesses are small businesses.
I would venture to say that there is a sizable portion of the population that if not already running a business, want to start one. Based on that, I am going to provide some tips to get started and hopefully avoid pitfalls that I have run across in my business dealings.
Select your partners well. This seems obvious, but you need to ensure that goals are aligned, that you want the same things for the business. Make sure that you can work with your partners. Make sure that your personalities do not clash. Make sure that all partners are able to understand viewpoints that are different from their own ideas and give them thoughtful consideration. Put a plan together for how you will proceed and have everyone sign off on it. Avoid partnerships where one or more partners are self-serving and attempt to obstruct ideas that do not favor them.
Define the duties of each partner for the business before investing any money, time, or effort. Agree on who does what and how it will be done. Have each partner provide a plan for how they will accomplish their duties. This seems a bit like overkill, but the effort put into this exercise will pay dividends in the form of getting each partner to think about what they will be doing and how they will be doing it. That alone is worth the exercise.
There are other types of legal entities, but this seems to be the most common structure used for small businesses. Depending on the type of business, you may be forced into using a C-Corp entity structure, such as a manufacturing business with inventory. While I am not an attorney and I do not play one on the internet, I am of the opinion that most small businesses are best served by an LLC structure.
In an LLC structure, the entity is considered a pass-through entity, so the profits of the company are passed through to the partners based on shares of equity in the company, to be reported on their personal income taxes.
With a C-Corp, the company is taxed, then dividends passed on to the shareholders (partners) is taxed again.
This is also a big one. The operating agreement can be based on the details pulled together in the Duties step. It just formalizes how the company will operate and documents the what & how for each partner. It also should contain exit strategies for each partner and for the company as a whole. This is probably more geared towards an LLC entity, but also has relevance to shareholders in a small private C-Corp.
If you already have a good idea for an entity name, then obviously, use it. But if you don’t, there is no need to stress out over it. Pick a name and as long as it is not already in use or trademarked, it will be good. If you later want have specific company branding/marketing, you can create a “Doing Business As” or DBA name. In most cases, all you have to do is file a form with the state for it to be recognized.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses the employer identification number or Tax ID as an identifier for businesses so they can track income and revenue. It costs nothing and can easily be applied for online.
Depending on the nature of your business, you may need to get a parish, county, or city business license. They are usually just a nominal fee, but not a whole lot. (Caveat: larger cities may have more exorbitant fees).
Always use a business bank account for your business finances. Keep your personal finances separate from your business finances. This will help to keep track of how well your business is doing.
For accounting purposes, you can start out tracking everything in a spreadsheet. Document revenue, document expenses. Depending on the nature of the business, you may need to do a little more than that and use an accounting software program or service. Once you reach a level where revenue and cash flow allow it, accounting tasks can be delegated to a book keeper.
I would also like to recommend using a CPA for filing your taxes. Having a good CPA on board will keep you out of trouble. Especially if a partner decides it is someone else’s job to get all documentation to said CPA at tax time. The CPA will file an extension on your behalf to keep you out of trouble.
And, as always, let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
This week is a bit of a follow-up to last week’s article about finding your breakeven point. I covered what you needed to look at and why it was a good idea to know what your breakeven point was before you get into a business. Now I will apply similar principles to Real Estate Investing.
Today, I am going to go over what I look at when I evaluate a property to add to my portfolio. My strategy for real estate investing is Buy and Hold, meaning that I buy properties and intend to keep them long term, renting them out to tenants.
For cost assumptions, I use the asking price, and an estimated cost of improvements (rehabbing property) & estimated closing costs (approximately 3% of price of property).
Use a mortgage calculator to determine monthly debt service payment. Set the desired term (15 yrs, 20 yrs, 30 yrs, etc.), down payment, and interest rate.
Gross Rents are the total rents expected to be collected on a monthly basis. This can be rent form a single-family home or a multi-family property such as a duplex, triplex, or larger apartment property.
To account for vacancy and deduct a percentage from your gross rent before deducting expenses. I generally use a conservative vacancy percentage like 10%. While I will more than likely not have 10% vacancy in a year, accounting for it helps me to ensure the property will always cash flow.
So, once I have a property to analyze, the first thing I do is verify the expenses. For the most part, the costs should be relatively the same, with the exception of property taxes.
I account for the following expenses:
Property Taxes can usually be found on the local parish or county assessor’s website. You just have to search for the property address and all of the details for the property are listed. Who owns it, what municipal assessed value is, what the property has sold for, and what the city and parish/county taxes are estimated at for the current year.
Insurance can be estimated by getting a quote from your insurance agent/provider or if you have a similar property, you already have an idea what the cost is.
Maintenance & Repairs covers anything short of replacing major components of the property.
Utilities are what you expect to pay for utilities while doing turnover or when the property is unoccupied between tenants.
Advertising is the costs for paid advertising to attract tenants.
Administrative are the costs for anything administrative to do with operating the property as a rental. This covers book keeping, accounts payable, accounts receivable, etc.
Variable Cost Property Management is a percentage of gross rents paid to a property manager to manage the property. I account for this as an expense even though I manage my own properties so in the event I decide to engage a property manager, I already have that cost covered and don’t have to worry about adding a PM cutting into my cash flow.
Lawn Care/Landscaping covers grass-cutting when the property is not occupied and/or if the property is a multi-family property where the tenants don’t normally take care of the lawn.
CAPEX is an amount put aside to cover major repairs such as replacing the roof, appliances, flooring, plumbing, electrical, etc. That way, you have the money to cover these repairs instead of worrying where to get the money from.
Once I have gross rents, vacancy, cost assumptions, and expense values collected, then the analysis of the property can begin. I use a spreadsheet to conduct my analysis and it is set up to tell me what I need to know. There are inputs for all of the items listed so far.
I enter the asking price, my desired finance terms, estimated gross rents, and estimated expenses.
I then evaluate whether or not my targets are met at the property’s asking price. If it does not, I then start adjusting the price downward until I reach my target numbers.
For me to consider a property a good deal, it must meet the following criteria:
Cash flow >$100 per door and have >12% Cash on Cash Return, if financed
Cash flow >$400 per door and have >6% Cash on Cash Return, if purchased cash
Be in a decent neighborhood
Cash Flow
Cash Flow is the amount of money from gross rents (revenue) remaining after expenses and debt service are covered.
Cash on Cash Return
Cash on Cash Return is the annual amount of return you get compared to the amount of cash you spent to acquire the property.
By comparing gross rents, total costs, expenses, debt service, and returns I am able to decide if a property will be a money-making addition to my portfolio. By continuing to add properties to my portfolio that cash flow, I get closer to my “Freedom Number”. Where my passive rental income covers my personal costs and expenses, so I don’t have to worry about needing a job.
And, as always, let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
 |
| “The break-even point (BEP) in economics, business—and specifically cost accounting—is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal.” |
This week’s topic is knowing your costs for your business or the Break-Even Point (BEP).
Before starting a business (or buying one), you should understand what your Break Even Point is. The BEP is where you have enough revenue coming in to cover all of your expenses. It means $0 in profit, but also that all expenses are covered.
Knowing what your BEP is can be beneficial in evaluating how much of your product or service you will have to sell to begin generating profit. It is always better to have this information before engaging in a business rather than trying to figure it out after you are already involved.
Direct Expenses
When determining the BEP, there are some differences between how to calculate this information for a Service Business and a Manufactured Products Business.
The next step is to gather all of your indirect expenses. This can include rent, utilities, sales, and distribution expenses. Anything that is not directly involved in the provision of a service or the manufacturing of a product.
Once you have all of your numbers, you can calculate your BEP.
For Service Businesses, your BEP is the sum of your direct and indirect expenses. If you bring in enough revenue to cover just those expenses, you have broken even.
For Manufactured Products Businesses, you simply divide your indirect expenses by your GP % to arrive at your BEP.
Example: Indirect Costs: $20,000; GP: 31%; $20,000/0.31= $64,516.13
As I stated above, it is a good idea to have this information before you are involved in a business. Once you understand where you stand with reference to a BEP, you can start to work on optimizing you costs & methodologies to increase efficiencies, lower costs, and lower the overall BEP for that business.
And, as always, let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
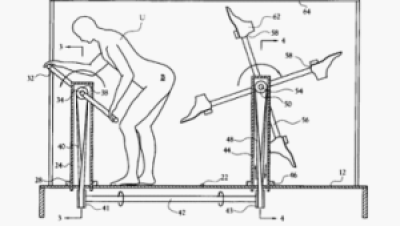 |
| Image from US Patent #6,293,874…”User-operated amusement apparatus for kicking the user’s buttocks” |
Today I am going to cover some things that we experienced last year while rehabbing a house acquired to become a rental.
This was our first acquisition, so I wanted to be thorough in analysis, planning, and execution. I had a home inspector check for problems with the house. He checked the electrical, cooling, foundation, plumbing, water heater, and roof. Issues were pointed out with the electrical, gas valves, air conditioner ductwork, and a couple of other minor things.
I brought in the following for estimates:
I thought I had things well covered. I was wrong. The first shock was that we had to replace the whole interior HVAC system. The furnace part was rusted through and a fire hazard. That wasn’t too bad, as we had a buffer in our budget for overages and $4,200 wasn’t going to kill it. (That price did include replacing the duct work.)
The next surprise was after the first tenants moved in, they attempted to wash clothes and the washer drain overflowed into the utility room. A phone call to the plumber and a day of trying to unclog the drain, it was determined that years ago, when the neighborhood was converted over to municipal sewerage, the original owners never bothered to tie in the utility room drain to the main drain line and just left it connected to the main field drain in the back yard, which had since collapsed, thus restricting flow and backing up into the utility room. Add another day for the plumber to route a drain through the wall and across the back patio (most likely the condemned septic tank) and tie it into the main drain line at a total cost of approximately $700.
Caveat: We will have to eventually add a full drain line underground tied into the main system.
#SilverLining: We will now have the drain necessary to convert part of the utility room to a half bath at some point, increasing the value and desirability of the property.
At one point, the original owners of the house upgraded the windows to vinyl double-paned glass. In doing so, there were gaps in between the windows and the sill in some rooms. I notice them, but in triaging everything that needed to be done, they kept falling to the bottom of the priority list. And, they never got done. Additionally, we kept finding wasps in the room where the gaps were the biggest. It seemed unrelated. The tenants actually correlated the gaps with the wasps continuously appearing in that room and asked for me to fix it. It didn’t take more than some expanding foam and caulk, but, like the other items listed here, I should have recognized the issues and fixed them prior to the tenants moving in. Total cost for the fix: about $25.
So, for the next property we purchase, I will make sure that we check all drains for restrictions, ensure all trim are sealed, and plan to continue to have the HVAC contractor evaluate the heating & cooling system. This will help to save extra work that we did not budget for and aggravation for us and the tenant in getting the issues mitigated.
If you have rental property, have you run into things like this? Let me know in the comments below.
And, as always, let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
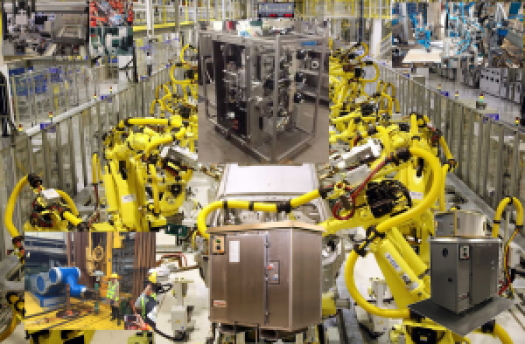 |
| Various pictures of industrial and oilfield automation. The bottom center, top center, and bottom right images are of the DRU. |
Let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
 |
| Actual picture from one of our properties. |
One of the last things you want to do is to get scammed as a real estate investor. It will happen if you are not prepared and do not have systems and processes in place to keep you from getting scammed.
When we decided to turn my in-laws house into a rental, we started to look for contractors to do the rehab on it because I was too busy with work to do it myself (and I wasn’t that great at what was needed anyway).
We asked around on Facebook, but didn’t get a whole lot of suggestions. A friend of a relative could do some of it, but we wanted to get someone to do all of the work.
My wife heard an advertisement on a local radio station for a home improvement contractor, so we called him to get a bid. He gave us a fairly cheap bid and said he could start working immediately. We decided to use him. (Mistaken Thinking #1: Since he was advertising on the radio, he must have been a legitimate contractor.) He told us he was licensed and insured, so we believed him (See mistaken Thinking #1). He then asked for a 30% down payment to be able to purchase materials, so we paid him the down payment. (Mistaken Thinking #2: It’s OK to pay a down payment before work starts.) After six weeks of no work being done except removing the one piece of baseboard and shoe molding in the picture above, in addition to him coming to us for additional material draws (that we paid), we finally realized that he wasn’t going to do the work.
We suspected something was up after four weeks, but didn’t want to believe it. Thankfully our state has a contractor Fraud law and between our complaints and complaints of other victims from surrounding area, there was enough to arrest him. He made a plea deal and has paid back almost half of the money he owes us.
We eventually found a really good contractor who came in and rehabbed everything in the house for us in about a month for a really good price. And we have been renting out the property ever since.
Let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
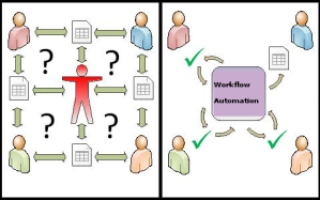 |
| Left: Manual Process; Multiple queries to multiple parties. Right: Workflow Automation directs processes smoothly. |
A couple of weeks ago, I was looking into tools to help automate workflows, preferably online tools. My initial premise was that I wanted to be able to track steps, tasks, and procedures in our real estate investing.
The more I thought about this, I realized that by combining Slack with something like Trello for the manufacturing business, we could achieve a few long-term goals. Trello actions could be reported into a Slack channel, giving us, (investment partners), a simulacrum of a real time dashboard of what is going on with orders in the manufacturing business. A similar setup could be made for product quotes. Slack channels could be used for communication between employees, management, and investors, respectively. Other channels could be used for Knowledge Management (KM)…a living archive of answers, best practices,documents, etc. I think I will call that channel #stunt_brain!
There are other options for automation and integrating various online applications like Podio, Zapier, and Zoho CRM. I haven’t played with them much, so I can’t really say a whole lot about them other than they exist.
Hopefully this has given you some insight into what I thought to be cool tools to bring efficiency to your workflow.
Let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
 |
| Like the game Monopoly, you can grow your money with Real Estate. |
This week, we are going to talk about how we started investing in real estate. It wasn’t an overnight decision, or result, for that matter.
My first foray into real estate investing (REI) was to partner with one my uncles and my cousin (his son) to develop an RV park in the Port Fourchon area. It seemed like a great idea…lots of potential for revenue and extended development. And I knew nothing about evaluating the deal to see if it was going to be a money maker or not. I put up the money to initiate the lease of the land ($20,000) and we proceeded to get a loan from a local bank to develop the park. We had to get permits, evaluations, inspections, etc. The total amount from the bank came to $150,000. Just as the park was about to open, the BP Macondo/Deepwater Horizon oil spill happened and shut down the oil & gas industry in the Gulf of Mexico. The space was leased to a catering company as a staging area for feeding spill cleanup workers and to facilitate a training space.
We eventually opened up the park and began operating. My cousin and his wife managed the operations.
I began traveling around the world a good bit for work and realized that I could not be deeply involved in the deal in addition to my wife not being happy with me involving us in it in the first place. My cousin offered to buy us out for $30,000, paid over time. This worked for us as it got our money back, along with about a 17% total ROI.
While the deal made us money, the stress and aggravation of not being in control left us with a bad taste in our mouths.
Fast forward a couple of years and we decided to remodel my in-laws’ home to set up as a rental. My father-in-law passed away the preceding year, leaving the home to my wife. We got it remodeled after a few false starts and bumps in the road. And started renting it out.
I mostly stayed hands-off of the operations and mainly just helped handle repairs & stuff, since it was my wife’s house (via inheritance).
Towards the end of 2015, I started to get aggravated with my job, (for the nth time), and started a more serious search for something else that I could rely on for income. In January of 2016, I found Bigger Pockets, an online forum/educational platform for real estate investors. It was then that I realized that REI was something that I could do. In fact, in a way, we were already doing it. The thing that appealed to me about it was that successful investors rely on systems and processes to make their businesses run well. WOW! I am a “Systems & Processes” type of guy! It was an epiphany, of sorts.
I started listening to podcasts, devouring forum posts related to my topics of interest, attending real estate investor association meetings, and reading books to learn about how to reach my financial goals through REI. I put together a 30,000 foot overview of what I would like to do and how I could do it. When I discussed my idea with my wife, she was initially skeptical because I repeatedly come up with plans to make money and either never initiate them or follow through on them.
I continued to learn about buying and managing rental properties, along with operating a business. I became more involved in the operation of the existing rental, more or less making it my responsibility.
So, that is how we got started in REI.
Let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.
 |
| What I grew up seeing around me. |
 |
| What I wanted to do. |
Today I am going to relate my experiences with Money from when I was a child to present day, in a loose chronological order.
My parents split up when I was approximately 10 years old and I don’t really remember a whole lot about our finances prior to that. What I do remember is that after that point, things were not easy.
We moved in with my grandparents, away from friends and family, started a new school, and began a different life. At the end of that school year, I began an unwanted tradition of working every summer on one of my grandfather’s shrimp boats and later in my uncles’ seafood businesses. Whatever money was earned went to help cover costs for my mother, my sister, and me to survive. I would get a hundred dollars at the end of the summer to buy school clothes for the upcoming year and that was the about all I would see of what I made.
My cousins of a similar age were doing the same work as me, but they got to keep all of their money, spending it on nice stereos, toys, etc., because their parents were making money and running a business.
I started learning about the businesses because it seemed like the way to not be poor. What I learned, besides the mechanics of actual operations, were bad money management habits.
Things seemed to be all about making sure you got your share out of the revenue, to the detriment of everything else…spending the holidays at hunting camps, spending the last bit of money you have, with no guarantee of future revenue.
This is not a good model to follow, especially if you are trying to maintain a steady income, much less, grow your income. Eventually, within a few years, both uncles were out of money, with no business to support them, because they only focused on the “right now” and had trouble planning for the long haul.
The takeaway lesson from today’s post is to not spend everything you make. Practice restraint and plan for the future. Short of winning the lottery like a former co-worker, you will not get rich quick. BUT, if you practice this as a habit, it should allow you to prepare for retirement.
Let me know what you think in the comments. Ask questions, tell your story.
If you like my posts, please share them with others and subscribe to this blog.